课题案例系列之:
抑菌材料
(Antibacterial materials)
案例简介>>
抑菌材料主要是指基于传统材料骨架添加各类新型因子而形成的新型复合材料。
目前主要做过的材料如下:
- 传统水凝胶的基础上添加金属离子(Cu、Ag、As、C、Co等)形成的新型抑菌材料,研究其体外抑菌作用、体内安全性、体内埋置等;
- 纳米纤维复合材料中添加抗生素、治疗药物等形成的新型复合材料,研究其体外抑菌作用、细胞粘附性、肿瘤细胞杀伤等;
- 新型纳米颗粒如Fe3O4偶联其他药物后而形成的新型可吞噬材料,研究其体外抑菌作用、细胞靶向性、细胞吞噬情况等;
- 类骨材料载药后而形成的新型骨替换材料,研究其体外抑菌作用,胶原细胞附着、体内修复作用等;
技术路线>>

结果展示>> Fig1
A B C D

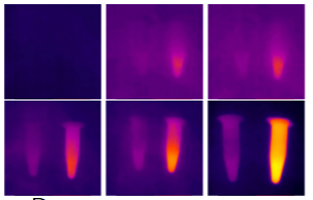
E
A. After adding new factors to the material, the viscosity and adhesion become stronger;
B. The new material can significantly heat up due to its absorption of specific wavelength light after adding special factors.
C. The drug carrier material can stably release the drug carried;
D. Analysis of the main composition of materials;
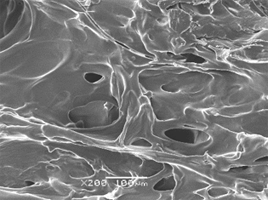
E. New materials undergo spatial changes due to the addition of specific factors.
技术路线>>
结果展示>> Fig2
A B C D E
F
|
OD405
|
调零
|
均值
|
|
溶血率
|
|
空白材料
|
1.315
|
1.276
|
1.326
|
1.306
|
|
24.200 %
|
|
新材料A
|
0.573
|
0.601
|
0.599
|
0.591
|
|
7.269 %
|
|
阴性
|
0.278
|
0.285
|
0.290
|
0.284
|
|
|
|
阳性
|
3.977
|
4.437
|
5.098
|
4.504
|
|
|
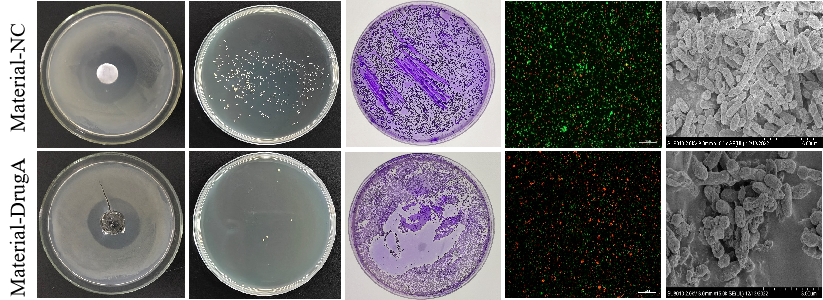
A. The new material has stronger antibacterial effect due to the addition of new factors, and the antibacterial zone is significantly increased;
B. The new material has stronger antibacterial effects due to the addition of new factors, making it almost impossible for bacteria to grow on it, resulting in almost no living bacteria in the eluate;
C. The drugs released by antibacterial materials have a great destructive effect on the biofilm and have a significant antibacterial effect;
D. The drugs released from antibacterial materials have a significant inhibitory effect on bacteria, and dead bacteria can be stained red by PI due to enhanced membrane permeability;
E. The drugs released from antibacterial materials have a significant inhibitory effect on bacteria, causing bacterial shrinkage and cell membrane dissolution on the materials, leading to cell apoptosis;
F. The release of new materials has no impact on hemolysis;
技术路线>>
结果展示>> Fig3
A B C
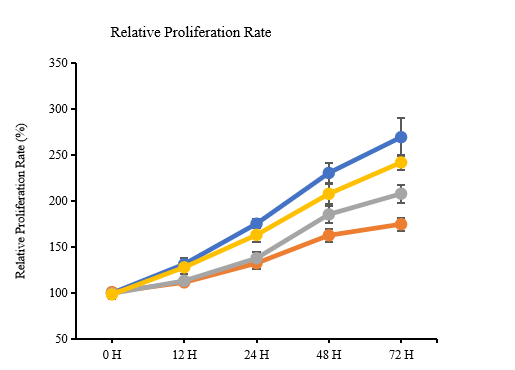

A. The CCK proliferation curve verifies that cells undergo apoptosis when attacked by bacteria, and the new material can release more antibacterial molecules to rescue this process;
B. The flow cytometry apoptosis experiment verifies that cells undergo a large amount of apoptosis when attacked by bacteria, and the new material can release more antibacterial molecules to rescue this process;
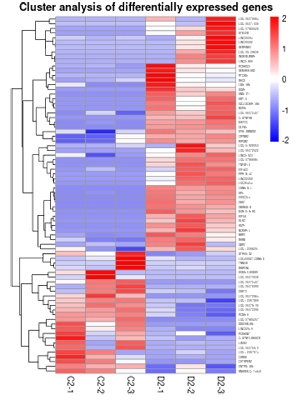
C. The mRNA sequencing results reveal specific response signaling pathways. Comparing the model group with the blank group, mRNA sequencing screened for significantly up-regulated or down-regulated factors, thus suggesting the possible pathways through which antibacterial materials may achieve cell protection mechanisms
技术路线>>
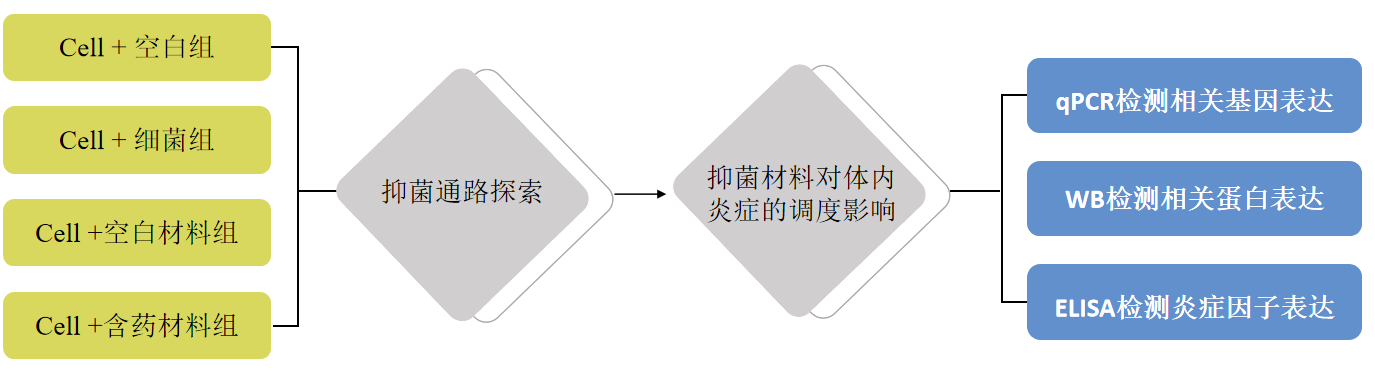
结果展示>> Fig4
A B C D
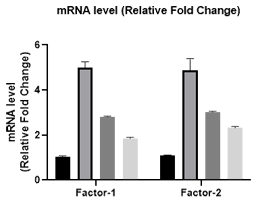
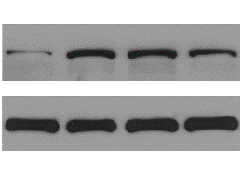
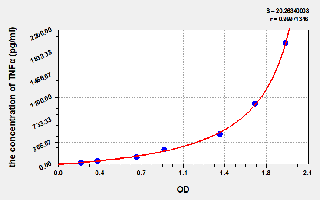
A. RT-qPCR detection explores the specific pathways of action of antibacterial materials at the mRNA level to protect cells from bacterial invasion;
B. WB detection explores the specific pathways of action of antibacterial materials at the protein level to protect cells from bacterial invasion;
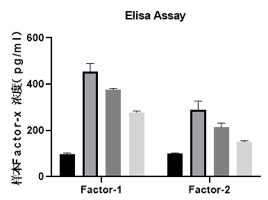
C. Biochemical Elisa verifies that cells are protected by new materials to avoid excessive inflammatory reactions.
技术路线>>
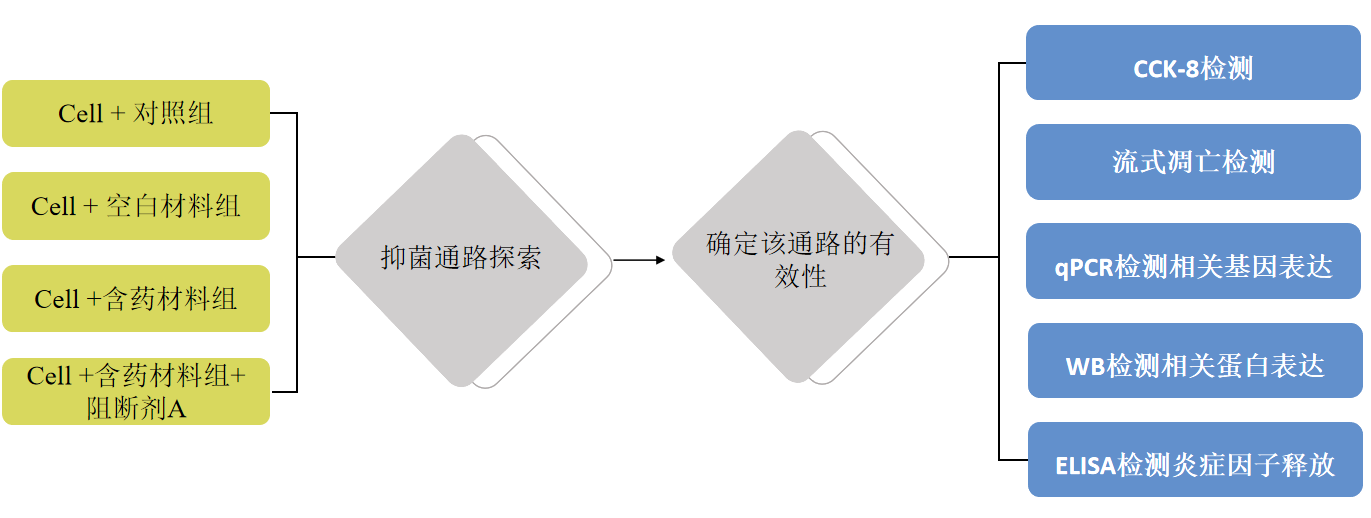
结果展示>> Fig5
A B
C D E

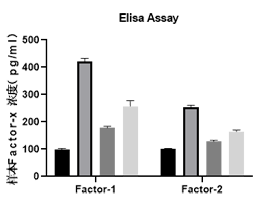
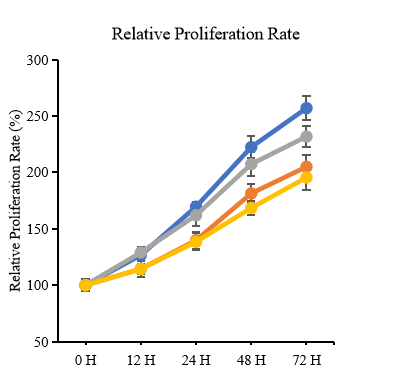
A. CCK8 proliferation level verification: The new material specifically protects cells from bacterial invasion through which pathway;
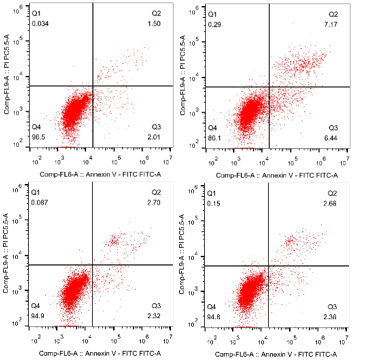
B. Flow cytometry apoptosis level verification: The specific pathway through which the new material protects cells from bacterial invasion;
C. Cell ferroptosis can be reversed by overexpression of the target protein, and the blocker of the target protein can block this process, resulting in the recovery of ferroptosis related protein factors. This experiment detected the expression of related proteins in cells through Elisa's method;
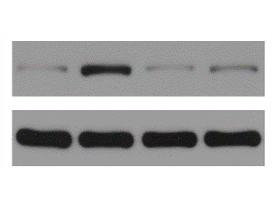
D. The protein level validation of the novel material specifically protects cells from bacterial invasion through which pathway;
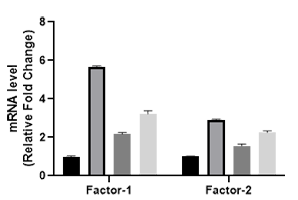
E. Elisa Assay detects protein factor levels and verifies which pathway the new material specifically protects cells from bacterial invasion through;
技术路线>>
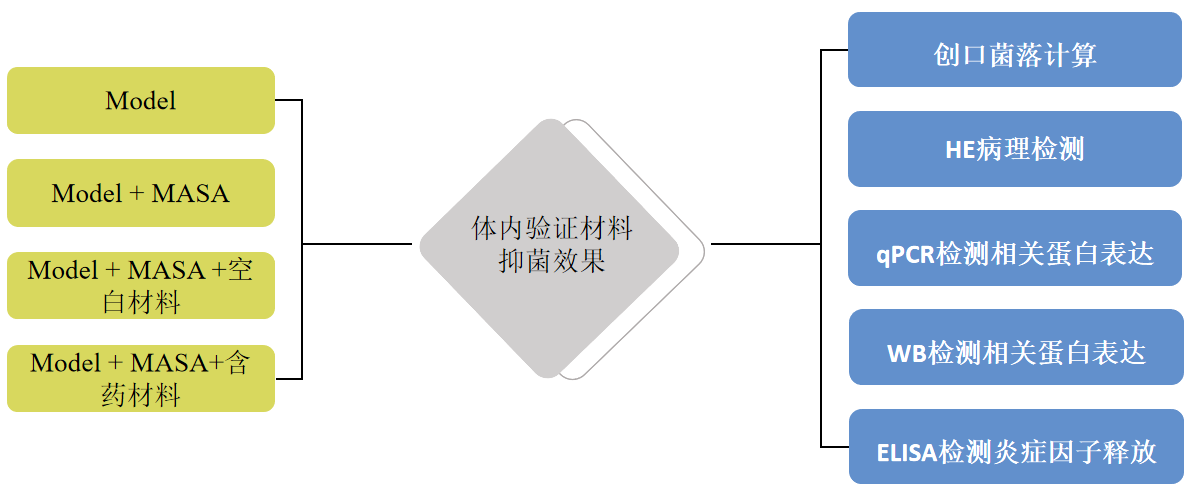
结果展示>> Fig6
A B C D E
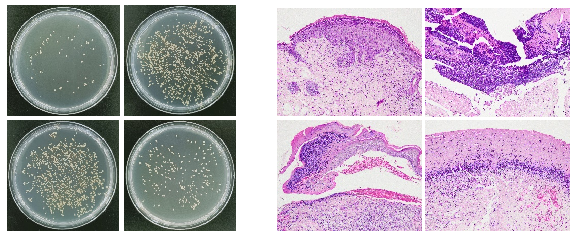



A. In vivo experiments shows that new materials can release more antibacterial molecules to inhibit bacterial growth, thereby helping the matrix avoid inflammation caused by bacteria;
B. The HE results show that the new material helps the matrix to prevent inflammation caused by bacteria;
C. The WB results verify that the new material can release more antibacterial molecules to inhibit bacterial growth, thereby helping the matrix avoid inflammation caused by bacteria;
D. RT-qPCR detection verifies that the new material can release more antibacterial molecules to inhibit bacterial growth, thereby helping the matrix avoid inflammation caused by bacteria;
E. Elisa Assay confirms that the new material can release more antibacterial molecules to inhibit bacterial growth, thereby helping the substrate avoid inflammation caused by bacteria.
在线咨询































